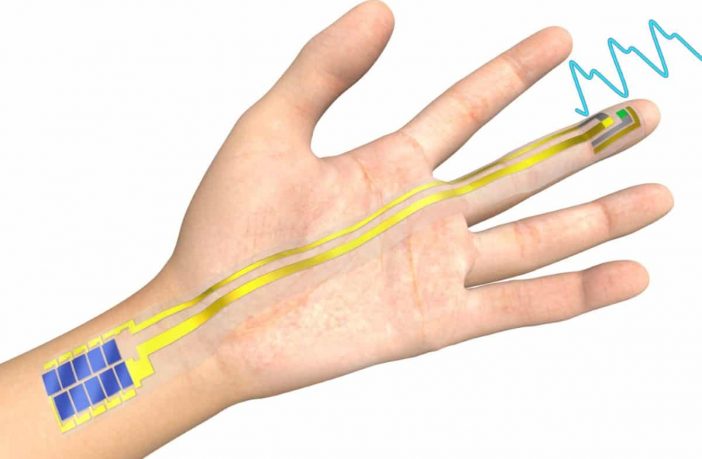
- Scientists from the Hiroshima University and the University of Tokyo in Japan have developed an ultrathin self-powered organic optical system for applications in the monitoring of photoplethysmogram (PPG), which is an optical technique used to detect volumetric changes in blood in the peripheral circulation.
- It is a non-invasive technology that utilizes a light source and a photodetector at the surface of the skin to measure the volumetric variations of blood circulation and is also used for heart rate monitoring.
“Our device can be fabricated using conventional methods including the printing process,” research co-author, Tomoyuki Yokota, told pv magazine. “It means that the limiting factor of the cost is material, which is organic semiconductor itself and if organic solar cells are widely used in society, the cost of devices will be reduced.”
The system, which is just a few microns thick, was built with an organic solar module, a polymer light-emitting diode (PLED), and an organic photodetector.

The PLED is powered by an organic module with 10 series connections that showed a 28.1% efficiency with 1000 lux of fluorescent lamp illumination under indoor light. “This value is equivalent as power output of 78.2 µW/cm2 whereas power output under 5000 µW/cm2 simulated sunlight is 290 µW/cm2,” the scientists explained. “With these results, our self-powered PPG system should work under 1000 lux of indoor light with OPV modules of 4.5 cm2 device area.
”The PLED is activated when the OPV module is exposed to the light and can be shut off when the OPV module is placed in the dark.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that demonstrates the use of self-powered optoelectrical sensors in ultraflexible organic devices,” the academics noted. “This self-power technology used in this study will pave the wave of ultraflexible wearable optoelectronic devices which take an important role for future ubiquitous healthcare society.”
A detailed description of the device was offered in the paper Self-powered ultraflexible photonic skin for continuous bio-signal detection via air-operation-stable polymer light-emitting diodes, published in nature energy.
Author: Emiliano Bellini
This article was originally published in pv magazine and is republished with permission.