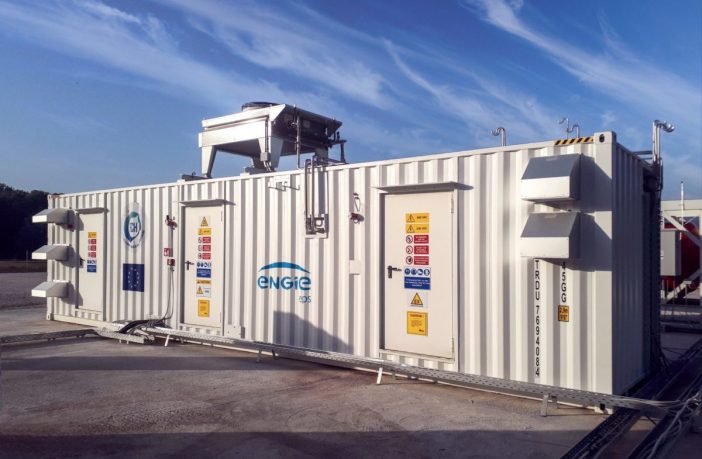
- Italy-based storage specialist Engie EPS, a unit of French energy giant Engie, has deployed a hydrogen-based storage solution for renewable energy storage in remote and off-grid areas, in Agkistro, in Greece’s northern regional unit of Serres.
The project was developed under the umbrella of the EU-funded H2020 Remote project (Remote area Energy supply with Multiple Options for integrated hydrogen-based Technologies).
The facility will enable Horizon, a Greek renewable energy company, to provide with power a local agri-food processing unit. Part of the energy produced by the nearby hydroelectric plant owned by Horizon will be converted into hydrogen and this hydrogen will then be stored and converted back into electricity according to the electricity needs of the plant.
The Engie EPS equipment in Agkistro consists of a hydrogen-based power-to-power system using an electrolyzer that converts electricity into hydrogen (power-to-gas), and a fuel cell system, which converts hydrogen stored in large quantities into electricity (gas-to-power), both based on Engie EPS proprietary technology, covered by more than 130 patents. The system will benefit from the continuous availability of renewable hydroelectric energy which allows the sizing of power-to-gas to be minimized while covering the peak demand for electricity and guaranteeing back-up energy thanks to the net energy equivalent to storage of 500 kWh of hydrogen. “Engie EPS has been a pioneer in the hydrogen sector since 2005 and has been at the forefront of battery storage systems and micro-grids since 2012,” said Carlalberto Guglielminotti, managing director of Engie EPS. “With the completion of the project in Agkistro, our proprietary hydrogen-based energy storage technology has now demonstrated on four continents that it is the only option available for the realization of 100% green micro-grids.
Looking forward, the company said it is targeting industrial scale opportunities as a systems integrator.
Author: Joël Spaes
This article was originally published in pv magazine and is republished with permission.